Ultraviolet disinfection can ensure sterilization effect and water quality. This is a long-term effective sterilization technology. No reaction, no rebound of flora, ensuring complete disinfection effect and water quality safety. Compared with other sterilization methods, UV has many obvious advantages, especially the difference from chemical disinfectants is that UV disinfectors will not bring toxic substances and residual substances into pure water, and will not change its chemical composition, breath and pH value. This function is very important in the pharmaceutical industry and related industries. The chemical dosage of influent often changes the characteristics of the product.
1. It can effectively kill all bacteria and viruses, and inactivate chlorine resistant microorganisms such as Legionella, Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas. Cryptosporidium, amoeba and bacteria.
2. During the disinfection process, no toxic and harmful by-products will be produced, the composition and performance of the disinfection water will not be changed, and no secondary pollution will be caused to the water body and the surrounding environment; Reduce the input of chlorine, reduce the residual chlorine, reduce the chlorine content in the swimming pool water, reduce the disinfection by-products, and make the swimming pool environment more healthy.
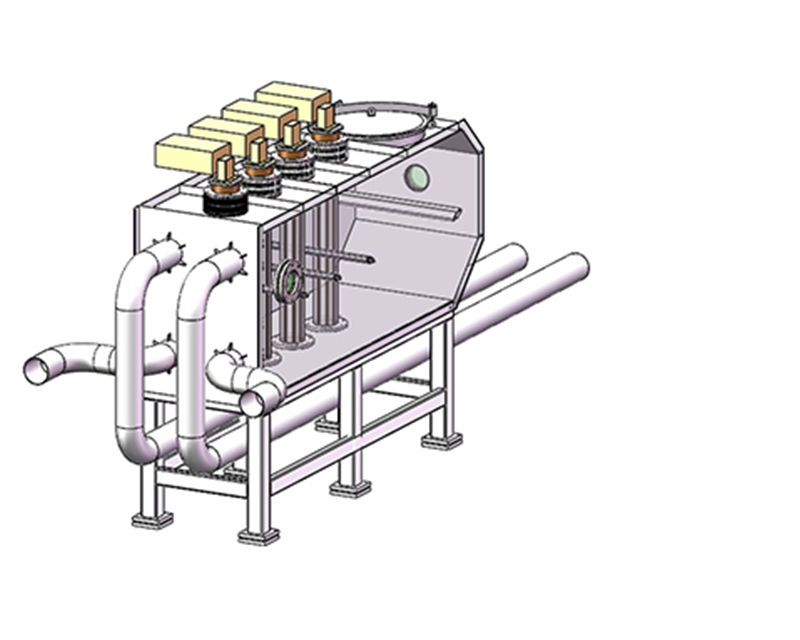
3. Small amount of space, safe and reliable operation, simple maintenance and low cost. It can be seen that UV sterilization has the advantages of sterilization, broad-spectrum sterilization, pollution-free, safe and reliable operation, and does not constitute a toxic by-product, so it is more and more widely used in engineering.
4. Usually, it can be completed in a few seconds. While destroying the DNA structure of microorganisms, it also synthesizes microorganisms into small fragments. It is precisely because of this ultraviolet sterilization characteristic that it can effectively prevent DNA reactivation and dark repair in microorganisms. Inactivated, no rebirth reaction, aseptic group rebound phenomenon.

